Urban Homicide Rates: Cities Outpacing Chicago in Violent Crime
Beyond Chicago: U.S. Cities with Higher Murder Rates
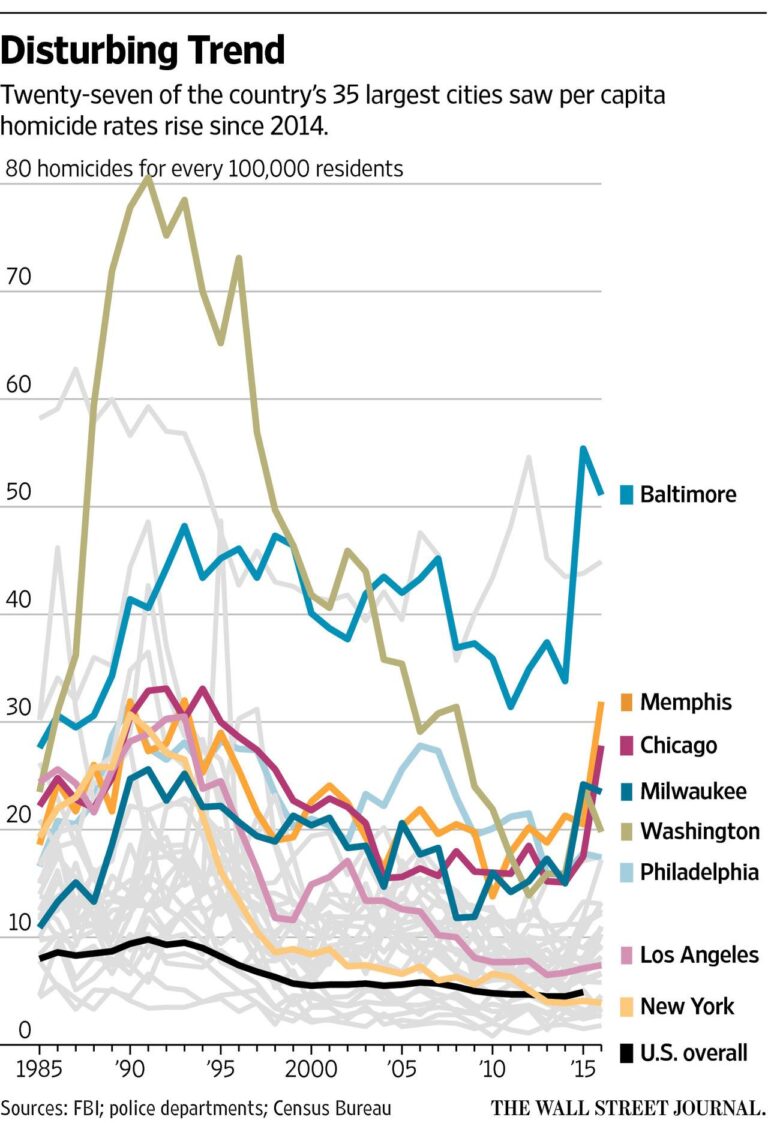
Chicago is frequently spotlighted in national media for its high homicide numbers, yet several other American cities report even more alarming murder rates. Urban centers such as Baltimore, St. Louis, and New Orleans have long struggled with deep-rooted social and economic hardships that fuel persistent violence. These cities demonstrate that the severity of violent crime is not always proportional to population size or media coverage. Instead, entrenched poverty, systemic inequality, and insufficient social infrastructure often underpin these elevated homicide statistics.
Examining homicide rates per 100,000 inhabitants reveals the following:
- Baltimore: Battles chronic poverty and drug-related violence, consistently ranking among the highest nationally.
- St. Louis: Experiences concentrated violence in specific neighborhoods, resulting in a homicide rate surpassing Chicago’s on a per capita basis.
- New Orleans: Endures long-term socio-economic instability that is reflected in its persistent homicide challenges.
| City | Homicide Rate (per 100K) | Population (Millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Baltimore | 58.3 | 0.6 |
| St. Louis | 59.8 | 0.3 |
| New Orleans | 45.2 | 0.4 |
| Chicago | 24.0 | 2.7 |
Root Causes: Socioeconomic and Policy Drivers of Urban Violence
Multiple economic and social factors contribute significantly to the heightened homicide rates observed in cities exceeding Chicago’s figures. Elevated unemployment often correlates with increased criminal activity, as financial instability can push individuals toward illicit means of survival. Additionally, limited access to quality education and healthcare disproportionately impacts marginalized neighborhoods, perpetuating cycles of disadvantage and vulnerability. Cities marked by stark income inequality frequently see violence escalate as disenfranchised populations compete for scarce resources and safety.
Policy frameworks also play a crucial role in shaping crime trends. Municipalities that implement community-centered policing and invest in social welfare programs tend to witness gradual declines in violent offenses. In contrast, punitive policies lacking community involvement can deepen mistrust and exacerbate tensions. Key factors influencing homicide rates in these urban areas include:
- Concentrated poverty and economic inequality
- Educational disparities and limited opportunities
- Firearm accessibility and regulatory environment
- Police-community relations and reform efforts
- Availability and funding of social and mental health services
| Contributing Factor | Effect on Crime Rates |
|---|---|
| Unemployment | Economic hardship increases likelihood of criminal behavior |
| Education | Lower educational attainment limits opportunities, raising violence risk |
| Gun Legislation | Weak firearm laws increase weapon availability for violent crimes |
| Social Services | Comprehensive support programs help reduce violence through community engagement |
Community Consequences: Public Safety and Quality of Life Impacts
Escalating homicide rates place immense pressure on law enforcement and community resources, often overwhelming their ability to maintain safety. Residents in these cities frequently endure increased fear and mistrust, which can fracture social bonds and depress local economies. Educational institutions and businesses face disruptions, leading to poorer academic performance and reduced commercial activity, thereby reinforcing cycles of poverty and instability.
Major challenges faced by affected communities include:
- Heightened fear restricting residents’ daily activities and freedom
- Strained emergency services resulting in slower response times
- Declining property values and diminished investment
- Limited access to safe public spaces and essential social programs
| Impact Area | Community Effects |
|---|---|
| Public Safety | Decreased confidence in police, delayed crime intervention |
| Economic Stability | Reduced business activity, job losses |
| Quality of Life | Increased stress, weakened social cohesion |
| Education | Lower attendance rates, fewer resources |
Effective Crime Reduction: Lessons from Cities Making Progress
Several cities grappling with high homicide rates have adopted innovative strategies that demonstrate promising results. These approaches include:
- Community Engagement Policing: Strengthening relationships between law enforcement and residents through regular neighborhood interaction fosters trust and cooperation.
- Targeted Deterrence: Concentrating resources on repeat offenders while providing alternatives to crime helps reduce violence without broad punitive measures.
- Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED): Enhancing public spaces with better lighting, removing blighted properties, and increasing surveillance discourages criminal activity by raising perceived risks.
- Data-Driven Resource Allocation: Leveraging analytics to identify crime hotspots enables proactive deployment of law enforcement and community resources.
When combined effectively, these tactics have led to significant reductions in homicide rates. The table below highlights select cities, their implemented strategies, and the percentage change in homicide rates over a recent five-year period:
| City | Primary Strategies | Homicide Rate Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Baltimore | Targeted Deterrence, Community Policing | -22% |
| St. Louis | Environmental Design, Data-Driven Policing | -18% |
| Detroit | Community Policing, Targeted Deterrence | -25% |
| New Orleans | Data-Driven Policing, Environmental Design | -20% |
Summary and Insights
Although Chicago frequently captures national attention for its homicide statistics, a broader analysis reveals that other metropolitan areas face even more severe violent crime challenges. Recognizing the multifaceted causes behind these elevated murder rates‚ÄĒincluding socioeconomic disparities, policy decisions, and community dynamics‚ÄĒis vital for crafting effective interventions. As cities continue to confront these complex issues, ongoing research, collaborative policymaking, and community engagement remain essential to reducing violence and enhancing public safety across the United States.