Texas Education Crisis: Unveiling the Challenges and Pathways to Progress
Analyzing Texas’s Educational Standing: A Comparative Overview
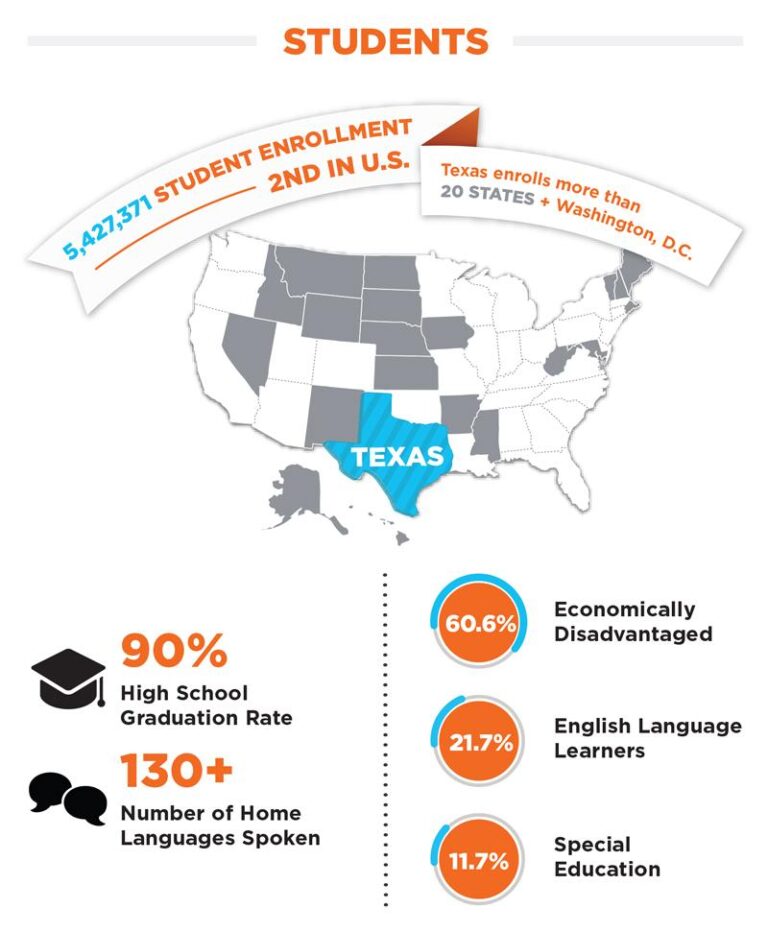
Recent analyses have spotlighted Texas as one of the states facing significant educational hurdles, trailing behind many others in key academic indicators. Despite nationwide improvements in graduation and college enrollment rates, Texas continues to struggle with lower percentages of adults holding bachelor’s degrees and slightly lagging high school completion rates. These disparities highlight systemic issues related to unequal access and attainment, influenced by factors such as funding imbalances, geographic divides, and socioeconomic challenges.
Highlighted data points from the latest educational report include:
- Only 29% of Texans aged 25 and older possess a bachelor’s degree, compared to the national figure of 35%.
- High school graduation rates in Texas stand at approximately 85.3%, just below the U.S. average of 88.1%.
- Post-secondary enrollment rates for recent high school graduates in Texas rank among the lowest nationwide.
| Educational Metric | Texas | U.S. Average |
|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree Holders | 29% | 35% |
| High School Graduation Rate | 85.3% | 88.1% |
| College Enrollment Rate | 62% | 68% |
Socioeconomic Barriers and Policy Obstacles Affecting Educational Outcomes
Texas’s educational challenges are deeply intertwined with socioeconomic disparities that disproportionately affect low-income communities. Economic hardship often translates into limited access to quality early education, overcrowded classrooms, and insufficient school resources. These conditions widen the achievement gap between students from affluent backgrounds and those facing poverty. Moreover, issues such as high child poverty rates and food insecurity create unstable learning environments, negatively impacting attendance and academic performance.
Compounding these challenges are policy-related difficulties. Texas’s heavy reliance on property taxes for school funding results in significant inequities, with wealthier districts receiving more resources than their less affluent counterparts. Additionally, debates continue over the effectiveness of standardized testing and curriculum frameworks, with critics calling for more equitable and adaptive educational models. Key challenges include:
- Disproportionate funding distribution driven by local property wealth disparities
- Insufficient statewide programs targeting early intervention and student support
- Challenges in attracting and retaining qualified teachers in economically disadvantaged areas
- Resistance to educational reforms that address the needs of diverse student populations
| Factor | Effect on Education | Relevant Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| Child Poverty Rate | Negatively impacts attendance and learning retention | 20.6% in Texas vs. 16.2% U.S. average |
| Per-Pupil Expenditure | Restricts access to quality educational materials and extracurricular activities | $9,400 in Texas vs. $13,000 national average |
| Teacher Turnover Rate | Disrupts continuity in instruction and mentorship | 15% annually in underfunded districts |
Consequences of Educational Deficits on Texas’s Workforce and Economy
The repercussions of Texas’s educational shortcomings extend beyond classrooms, significantly influencing the state’s labor market and economic development. A substantial portion of the workforce lacks the advanced skills required for well-paying, specialized occupations, limiting career advancement and innovation potential. Employers frequently report challenges in filling technical and professional roles, prompting reliance on talent from other states and hindering business growth. This dynamic perpetuates dependence on lower-wage sectors, affecting overall wage progression and residents’ quality of life.
Broader economic impacts include:
- Decreased productivity: Limited technical skills among workers reduce operational efficiency.
- Restricted industry diversification: Emerging sectors like technology and renewable energy face labor shortages.
- Increased social service costs: Higher unemployment and job instability drive public spending upward.
- Slower innovation rates: Insufficient skilled professionals curtail research and development efforts.
| Indicator | Texas | National Average |
|---|---|---|
| High School Graduation Rate | 82% | 88% |
| Adults with Bachelor’s Degree | 28% | 34% |
| Skilled Workforce Positions Filled | 65% | 77% |
Strategic Reforms Recommended to Elevate Texas Education
Education experts and policymakers advocate for a comprehensive transformation of Texas’s public education system to address entrenched inequities and improve academic outcomes. Central to these proposals is the expansion of access to quality early childhood education, reduction of class sizes, and increased financial support for schools in economically disadvantaged areas. Without such focused investments, Texas risks perpetuating its low educational rankings, which could undermine its economic competitiveness and social equity.
Beyond funding, there is a growing call to revamp curriculum standards and enhance teacher support mechanisms. Suggested reforms include:
- Incorporating culturally responsive teaching practices to better engage diverse learners
- Providing ongoing professional development centered on innovative instructional strategies
- Shifting accountability frameworks to prioritize holistic student success over standardized test scores
| Focus Area | Recommended Actions | Anticipated Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Equity | Increase state allocations to underfunded districts | Reduce achievement disparities |
| Teacher Development | Enhance training programs and improve compensation | Elevate teaching quality and retention |
| Curriculum Innovation | Adopt inclusive, adaptable educational standards | Boost student engagement and learning outcomes |
Conclusion: Addressing Texas’s Educational Challenges for a Prosperous Future
As Texas confronts its position among the nation’s least educated states, the urgency for strategic investments in education infrastructure, policy reform, and community engagement becomes clear. Tackling these issues is essential to preparing a workforce capable of meeting the demands of a dynamic economy. Collaboration among government entities, educators, businesses, and communities will be vital to reversing current trends and expanding access to quality education and lifelong learning. Though the road ahead requires dedicated effort, the potential rewards for Texas’s economic vitality and social well-being are immense.