Fort Worth Tops U.S. Cities in Population Growth Amid Thriving Economic Landscape
Fort WorthŌĆÖs Population Boom: Economic Drivers and Growth Catalysts
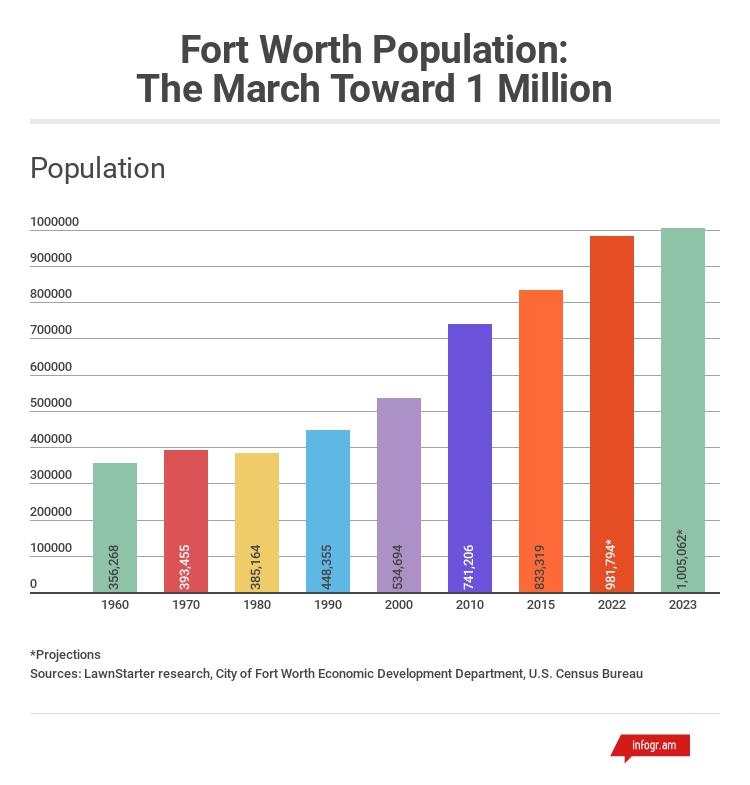
Fort Worth has surged ahead as the fastest-growing city in the United States in 2023, according to the latest figures from The Business Journals. This remarkable expansion is largely propelled by a flourishing economy that attracts a diverse range of industries and skilled professionals. Key sectors such as advanced manufacturing, healthcare services, and technology innovation have generated abundant employment opportunities, enticing individuals and families nationwide to relocate.
The cityŌĆÖs strategic focus on nurturing entrepreneurship and enhancing infrastructure has established Fort Worth as a vibrant center for both emerging startups and established enterprises. Several critical factors underpin this rapid growth:
- Cost-effective living: Significantly lower housing and living expenses compared to major coastal metros.
- Improved transit systems: Expansion of highways and public transportation networks enhancing regional connectivity.
- Business-friendly environment: Policies that incentivize investment and streamline regulatory processes.
- Strong educational framework: Quality universities and vocational programs fueling workforce readiness.
| City | Population Growth Rate (2023) | National Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Fort Worth, TX | 3.4% | 1st |
| Austin, TX | 3.1% | 2nd |
| Charlotte, NC | 1.5% | 15th |
| Dallas, TX | 1.2% | 24th |
Understanding DallasŌĆÖs Population Growth: Challenges and Opportunities
While Dallas ranks 24th among the fastest-growing U.S. cities, its population increase reflects a complex interplay of economic strengths and urban challenges. The city benefits from a diversified economy, with thriving sectors in finance, technology, and healthcare attracting a steady stream of young professionals and families. However, DallasŌĆÖs growth is moderated by higher housing costs and urban density issues compared to its neighbor Fort Worth.
Key factors influencing DallasŌĆÖs population trends include:
- Housing affordability: Elevated home prices and limited new construction slow migration inflows.
- Infrastructure development: Investments in transit and public amenities are ongoing but have yet to fully meet demand.
- Economic diversification: While broad, some industries face growth plateaus, impacting overall expansion.
| Factor | Effect on Growth | Comparison to Fort Worth |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Affordability | Moderate Growth | Less Affordable |
| Job Market Strength | Robust | Comparable |
| Urban Density | High | Lower Density |
| Infrastructure Progress | Developing | Rapid Expansion |
Infrastructure and Housing: The Ripple Effects of Fort WorthŌĆÖs Rapid Expansion
The swift population increase in Fort Worth is exerting significant pressure on the cityŌĆÖs infrastructure systems. Traffic congestion has intensified, with commute times rising sharply, prompting urgent calls for expanded public transit solutions. City planners are prioritizing projects such as roadway expansions and utility system upgrades to accommodate the growing demand. Additionally, water and sewage networks require immediate enhancements to sustain service quality amid the population surge.
The housing market is similarly impacted, with demand outstripping supply and driving up both home prices and rental costs. Although developers are accelerating construction efforts, challenges remain:
- Scarcity of affordable housing: Low- to middle-income families face limited options.
- Urban sprawl concerns: Expansion threatens natural green spaces and lengthens daily commutes.
- Rising building expenses: Material shortages and labor market tightness increase costs.
| Metric | 2019 | 2023 | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median Home Price | $250,000 | $375,000 | +50% |
| Average Commute Duration (minutes) | 24 | 33 | +37.5% |
| New Housing Permits Issued | 8,500 | 12,200 | +43.5% |
Pathways to Sustainable Urban Growth in North Texas
Addressing the rapid population increases in Fort Worth and Dallas requires comprehensive urban planning strategies that harmonize growth with environmental stewardship. Emphasizing transit-oriented development can alleviate traffic congestion and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by promoting public transit use and walkable neighborhoods. Expanding light rail lines and bus rapid transit corridors will better connect urban centers with expanding suburbs, fostering equitable access to jobs and services.
Smart zoning policies encouraging mixed-use developmentsŌĆöintegrating residential, commercial, and recreational spacesŌĆöcan curb urban sprawl and create vibrant, compact communities. Incorporating green infrastructure, such as urban parks and sustainable building practices, will improve air quality and enhance residentsŌĆÖ quality of life. The following table outlines key strategies tailored for North TexasŌĆÖs evolving urban landscape:
| Strategy | Primary Benefit | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Transit-Oriented Development | Lower Traffic Congestion & Emissions | Urban & Suburban Corridors |
| Mixed-Use Zoning | Walkable, Compact Communities | Emerging Residential Districts |
| Green Infrastructure | Enhanced Air Quality & Recreation | Parks & Urban Forestry |
| Affordable Housing Programs | Inclusive Economic Growth | High-Demand Neighborhoods |
Looking Ahead: The Future of North Texas Urban Development
Fort WorthŌĆÖs unprecedented population growth signals transformative shifts in the economic and infrastructural fabric of North Texas. While Dallas continues to hold a strong national position, Fort WorthŌĆÖs rapid ascent reshapes regional dynamics, influencing housing markets, employment landscapes, and urban planning priorities. Policymakers, developers, and community leaders will need to collaborate closely to ensure that growth is managed sustainably, balancing opportunity with quality of life for all residents in the years to come.