Shifting Domestic Migration Trends: What’s Behind the Decline in Americans Moving to Texas?
Understanding the Recent Drop in Domestic Moves to Texas: Economic and Social Influences
For decades, Texas has been a top destination for Americans relocating within the country, drawn by its robust economy and relatively affordable cost of living. However, recent statistics reveal a slowdown in the number of people moving to Texas from other U.S. states. This shift is largely driven by a combination of economic pressures and evolving social factors that are reshaping the state’s attractiveness.
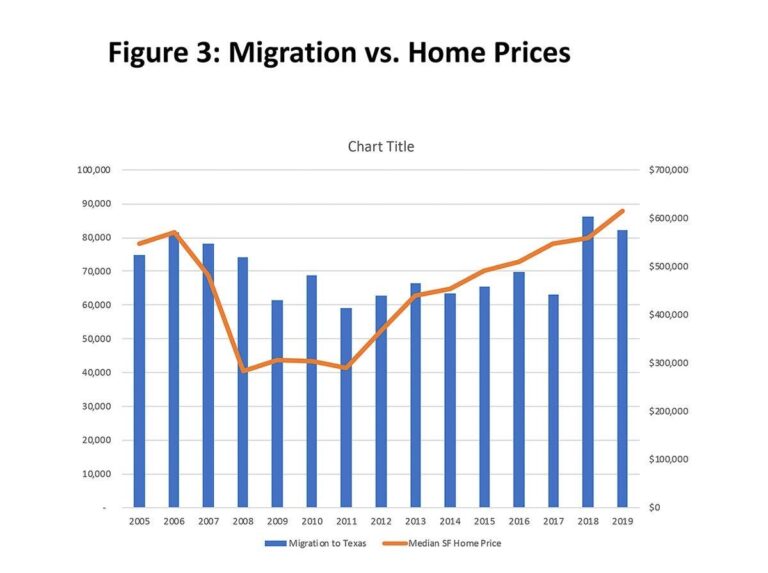
One of the primary economic challenges is the surge in housing expenses across major metropolitan areas such as Dallas, Houston, and Austin. The median home price in Texas has climbed approximately 25% since 2021, significantly narrowing the affordability gap that once made Texas a standout choice. Concurrently, wage increases have not kept pace with inflation and rising living costs, causing many prospective movers to reconsider the financial benefits of relocating.
Social considerations also weigh heavily on migration decisions. Texas’s political environment, which has become more polarized, influences perceptions, especially among individuals from more progressive states who prioritize social services and community inclusivity. Additionally, the pandemic-induced shift toward remote work has altered preferences for urban versus suburban or rural living, further complicating migration patterns.
- Higher property taxes and utility bills increasing monthly expenses
- Concerns over healthcare accessibility amid rapid population growth
- Challenges within the public education system impacting family relocation choices
- Political divisions affecting lifestyle and community fit
| Factor | Migration Impact | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Affordability | Significant deterrent | Median home prices up 25% since 2021 |
| Labor Market | Moderate influence | Wage growth trailing inflation rates |
| Social Environment | High influence | Shifts in voter registration and political engagement |
How Housing Market Pressures and Employment Trends Are Reshaping Texas Relocation Patterns
The rapid escalation of housing costs in Texas has become a critical factor discouraging new residents. With median home prices now exceeding $400,000 in key cities, many potential movers find the financial burden prohibitive. This is compounded by rising rental rates, which have surged by nearly 15% over the past two years, squeezing budgets for young professionals and families alike.
Employment opportunities, while still abundant in sectors like technology and healthcare, are increasingly concentrated in urban centers such as Dallas and Austin. This concentration limits job prospects in smaller cities and rural areas, reducing the incentive for relocation within the state. Moreover, the widespread adoption of remote work has diminished the necessity of moving for employment, allowing workers to remain in their current locations while accessing jobs elsewhere.
Additional pressures on urban infrastructure, including traffic congestion and strained public services, are also influencing decisions about where to live within Texas.
- Rising rental costs pricing out many renters
- Job market concentration limiting regional employment options
- Remote work flexibility reducing relocation urgency
- Infrastructure challenges impacting quality of life in growing cities
| Factor | Effect on Relocation |
|---|---|
| Housing Expenses | Lower affordability deters newcomers |
| Employment Distribution | Job opportunities concentrated in few metros |
| Remote Work Trends | Less need to relocate for jobs |
| Urban Infrastructure | Congestion and service strain reduce livability |
Demographic Shifts and Their Influence on Texas’s Urban Growth and Community Fabric
Texas’s demographic profile is undergoing significant transformation, with international immigration playing a larger role in population growth than domestic migration. Immigrants from Latin America, Asia, and other regions are increasingly shaping the cultural and economic landscape of cities like Houston and Dallas. This influx is fostering diverse neighborhoods and vibrant cultural districts, enriching the social fabric of the state.
These demographic changes are driving new demands in housing, education, and infrastructure. Suburban and peri-urban areas are seeing heightened demand for affordable housing options, while public schools are expanding multilingual and multicultural programs to serve a more diverse student body. Public transit systems and urban planning efforts are adapting to accommodate denser, more heterogeneous populations.
- Growing immigrant communities creating new cultural and business hubs
- Reduced domestic migration increasing competition for urban jobs
- Rising youth population boosting demand for innovative public amenities
| Demographic Trend | Community and Urban Impact |
|---|---|
| Increasing immigrant population | Emergence of multicultural neighborhoods and enterprises |
| Declining domestic migration | Heightened job competition in metropolitan areas |
| Expanding younger demographic | Greater need for modern public services and recreational facilities |
Adapting to New Realities: How Texas Cities Can Attract and Retain Domestic Residents
In response to the slowdown in domestic migration, Texas municipalities must innovate to remain appealing to potential residents. Prioritizing the development of affordable housing is critical, especially in rapidly growing urban centers where price surges have priced out many. Enhancing public transit infrastructure and promoting walkable neighborhoods can attract younger demographics and families seeking convenience and sustainability.
Moreover, diversifying local economies by investing in sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, and technology will create resilient job markets that appeal to a broad range of workers. Inclusive community planning that fosters cultural engagement and equitable access to resources will also be key to retaining newcomers and encouraging long-term residency.
- Affordable housing projects to support sustainable population growth
- Expanded public transportation to improve connectivity and reduce commute times
- Education and workforce partnerships to align skills with emerging industries
- Community development initiatives that enhance social cohesion and quality of life
| Strategy | Main Advantage | Key Participants |
|---|---|---|
| Affordable Housing Expansion | Encourages long-term settlement | Urban planners, developers |
| Public Transit Improvements | Boosts accessibility and reduces traffic | Transit authorities, commuters |
| Workforce and Education Programs | Builds a skilled labor pool | Educational institutions, employers |
| Community Engagement | Strengthens social bonds and well-being | Residents, local officials |
Looking Ahead: The Future of Texas Migration and Growth
As Texas experiences a deceleration in domestic migration, the interplay of rising housing costs, shifting job markets, and changing social preferences is redefining the state’s growth trajectory. While international immigration continues to fuel population increases, the evolving domestic migration landscape signals a new era for Texas’s urban development and demographic composition. How policymakers and communities respond to these challenges will shape the state’s economic vitality and cultural richness in the years to come.