Avian Influenza: U.S. Reports First Human Fatality ŌĆō Insights, Prevention, and Public Health Strategies
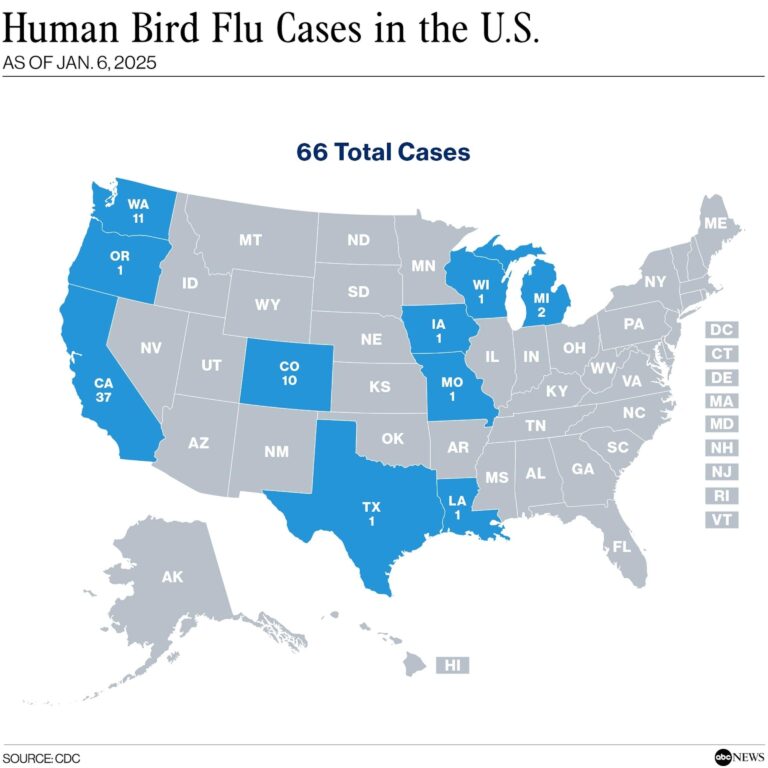
Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses that predominantly affect bird populations but can occasionally infect humans, sometimes with serious health outcomes. The recent fatality in the United States has been linked to the H5N1 subtype, a highly pathogenic strain notorious for causing severe illness in birds and sporadic human infections. Human transmission generally occurs through direct contact with infected poultry or contaminated environments, highlighting the critical need for stringent biosecurity measures on farms and cautious handling of birds. Symptoms in infected individuals often resemble severe influenza, including high fever, persistent cough, and breathing difficulties, making prompt medical attention essential.
How Avian Influenza Spreads and What You Should Know
The H5N1 virus primarily circulates among wild and domestic birds, but human cases arise when people come into close proximity with infected animals or contaminated surfaces. Unlike seasonal flu, bird flu does not easily spread from person to person, but the risk remains a public health concern due to the virusŌĆÖs potential to mutate. Recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate an uptick in avian influenza outbreaks among U.S. poultry farms in 2024, underscoring the urgency of preventive actions.
Practical Steps to Protect Yourself and Your Loved Ones
- Refrain from handling live birds or visiting poultry farms, especially in regions experiencing outbreaks.
- Maintain thorough handwashing routines after any contact with birds or farm environments.
- Ensure all poultry products and eggs are cooked to an internal temperature of at least 165┬░F (74┬░C) to eliminate viral presence.
- Keep abreast of updates from public health authorities and promptly report any suspected symptoms or exposures.
Current Public Health Initiatives and Preparedness Measures
| Public Health Initiative | Current Status |
|---|---|
| Intensified monitoring of poultry operations nationwide | Active |
| Educational outreach and risk communication campaigns | Ongoing |
| Stockpiling antivirals and vaccine development efforts | Prepared |
| Collaboration between federal, state, and local agencies | Implemented |
Summary and Future Outlook
The confirmation of the first human death from bird flu in the United States represents a pivotal moment in the surveillance and management of avian influenza. Health authorities continue to stress the importance of public awareness and adherence to preventive guidelines to reduce transmission risks. Ongoing investigations aim to better understand the virusŌĆÖs behavior and to strengthen containment strategies. For the most current updates and expert advice on avian influenza, rely on official health channels and reputable news outlets.