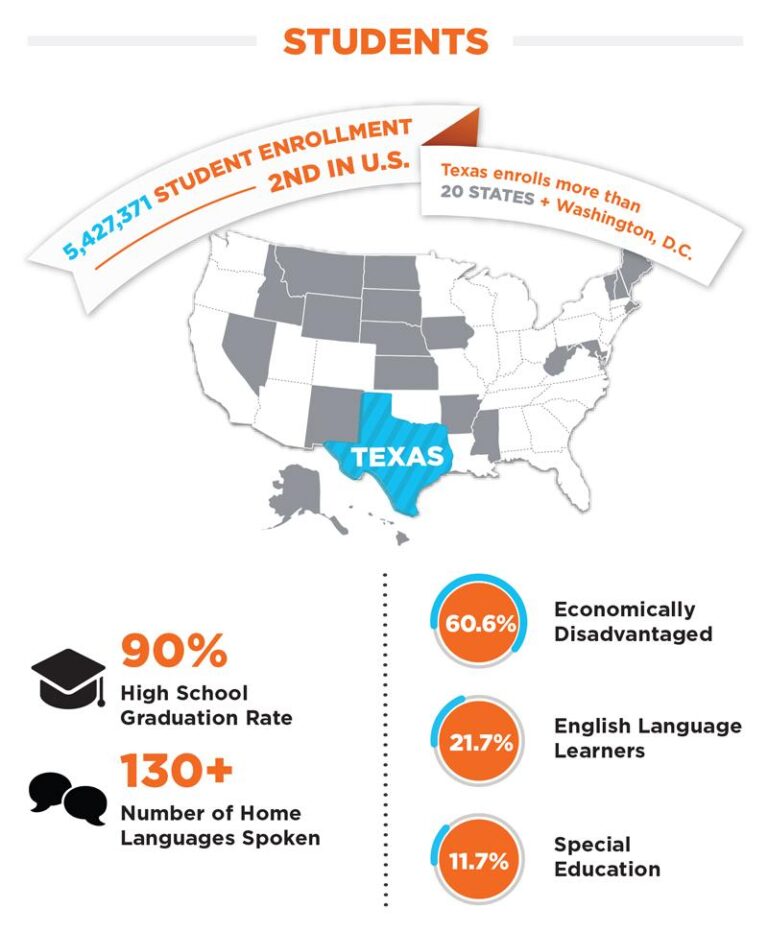
Addressing Educational Challenges in Texas: A Path Toward Equitable Learning and Economic Growth
Unearthing Educational Disparities Across Texas
Recent analyses have placed Texas near the bottom in national education rankings, spotlighting significant concerns about the state’s preparedness to cultivate a skilled workforce and sustain economic vitality. Despite Texas’ booming population and vibrant economic sectors, educational attainment remains uneven, with stark contrasts emerging among different communities. This disparity raises critical questions about equitable access to quality education and the adequacy of investments in academic programs.
Dissecting Academic Performance: Regional Variations and Underlying Causes
Data from the Texas Education Agency reveals a widening gap in academic achievement among students statewide. While some districts report improvements in graduation rates and standardized test scores, others lag behind due to entrenched socioeconomic challenges, racial disparities, and unequal resource distribution. These gaps threaten to undermine the state’s ability to prepare youth for future employment demands.
Primary contributors to these educational inequalities include:
- Disparities in funding between metropolitan and rural school districts
- Differences in teacher qualifications and retention challenges
- Restricted availability of advanced placement courses and extracurricular activities
- Insufficient support systems for students learning English as a second language
| Area | Graduation Rate (%) | Math Proficiency (%) | Reading Proficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Antonio | 83 | 46 | 49 |
| El Paso | 80 | 42 | 47 |
| Rural East Texas | 70 | 35 | 38 |
| Suburban Dallas-Fort Worth | 88 | 55 | 60 |
Economic Ramifications of Educational Shortfalls in Texas
The ongoing educational deficiencies in Texas pose significant risks to the state’s economic development and labor market efficiency. A workforce lacking adequate education and skills is less equipped to meet the demands of high-growth industries, such as renewable energy and biotechnology, which are increasingly vital to Texas’ economy. This skills gap restricts many Texans to lower-income positions, curbing economic mobility and dampening consumer spending, which collectively slow statewide economic progress.
Economic impacts stemming from low educational attainment include:
- Decreased innovation capacity and diminished competitiveness in cutting-edge sectors
- Greater dependence on low-wage service roles with limited advancement opportunities
- Escalated public spending on social welfare and retraining initiatives due to workforce mismatches
| Area of Impact | Economic Effect | Workforce Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Productivity | Reduced output per employee | Shortage of skilled professionals |
| Wage Growth | Flat income progression | Limited professional development |
| Technological Advancement | Slow adoption of innovations | Deficits in STEM expertise |
Distinct Challenges in Urban and Rural Texas Schools
Schools in Texas face unique hurdles depending on their geographic and demographic contexts. Rural schools often struggle with scarce resources, including a shortage of experienced educators, outdated instructional technology, and limited funding. Geographic isolation further complicates student attendance and engagement, hindering consistent academic progress.
Conversely, urban schools contend with overcrowding and a highly diverse student body requiring differentiated instructional strategies. High poverty rates and community instability exacerbate educational challenges, contributing to lower graduation rates and persistent achievement gaps.
| Challenge | Rural Schools | Urban Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Teacher Recruitment | Critical shortages | Moderate shortages with frequent turnover |
| Classroom Size | Small but isolated | Overpopulated and resource-limited |
| Technology Access | Often outdated or insufficient | Improving but inconsistent |
| Student Economic Background | High poverty, limited support services | High poverty, diverse educational needs |
Strategic Recommendations: Funding and Targeted Educational Programs
Education policy specialists advocate for a significant boost in state funding to tackle the entrenched issues revealed by recent studies. Without increased financial support, Texas schools will continue to face overcrowding, insufficient learning materials, and aging infrastructure. Emphasis should be placed on initiatives that provide focused assistance to vulnerable groups, including economically disadvantaged students, English language learners, and those in rural districts where educational inequities are most severe.
Proposed interventions aim to narrow achievement gaps and elevate overall student performance. These include expanding early childhood education access, enhancing teacher training with an emphasis on culturally responsive teaching, and integrating technology to support individualized learning experiences. Additionally, fostering partnerships with community organizations and expanding after-school programs can offer vital academic and emotional support.
- Preschool Expansion Grants: Increasing availability of early education in underserved communities.
- Professional Development Funding: Equipping educators with skills to address diverse learner needs.
- Digital Learning Resources: Providing schools with modern technology to enhance instruction.
| Initiative | Focus Group | Projected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Reading Readiness Program | Early Learners | Boost literacy rates by 25% |
| STEM Enrichment Mentorship | Middle School Students | Raise science and math scores by 18% |
| After-School Academic Support | High School Students | Lower dropout rates by 12% |
Looking Forward: Collaborative Efforts for a Brighter Educational Future
The data underscores the urgent need for Texas to confront its educational challenges head-on. Policymakers, educators, and community stakeholders must unite to implement comprehensive reforms and increase investments that promote equitable learning opportunities. Education remains a cornerstone for economic advancement, and improving Texas’ educational standing is essential to fostering a prosperous, competitive future. Through coordinated efforts spanning government, schools, and local organizations, Texas can build a more skilled, adaptable, and thriving workforce.